过氧甲酸
外观
| 过氧甲酸 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| IUPAC名 Methaneperoxoic acid[1] | |||
| 别名 | 过甲酸 过氧蚁酸 | ||
| 识别 | |||
| CAS号 | 107-32-4 | ||
| PubChem | 66051 | ||
| ChemSpider | 59441 | ||
| SMILES |
| ||
| 性质 | |||
| 化学式 | CH2O3 | ||
| 摩尔质量 | 62.02 g·mol−1 | ||
| 外观 | 无色液体 | ||
| 熔点 | -18 °C[2] | ||
| 沸点 | 50 °C[2] | ||
| pKa | 7.1[2][3] | ||
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |||
过氧甲酸(英语:Performic acid)是一种有机过氧酸,分子式为CH
2O
3。它是不稳定的无色液体,可由甲酸和过氧化氢混合制得。过氧甲酸有强氧化性和杀菌能力,被用于医疗和食品工业领域。
性质
[编辑]过氧甲酸在室温下是无色液体,可溶于水、醇、乙醚、苯、氯仿等有机溶剂[4][5]。因其具有强氧化性,被用于切割蛋白质中的二硫键[6],也被用于有机合成中的环氧化、羟化和氧化反应[5]。在医疗和食品行业,过氧甲酸被用于消毒,其对病毒、细菌孢子、藻类、真菌、分枝杆菌及浮游生物等都有效。过氧甲酸氧化后的降解产物为水、二氧化碳和氧气,因此会作为杀菌剂普及[4][7]。过氧甲酸的消毒作用快于过氧乙酸和过氧化氢[8]。
过氧甲酸的主要缺点是高反应性和不稳定性,因此其需要在合成后的约12小时内使用。此外,加热过氧甲酸是十分危险的操作[8][9][10] 。
合成
[编辑]过氧甲酸可以通过甲酸与过氧化氢的平衡反应制备:
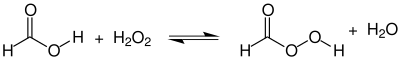
纯的过氧甲酸尚未制得[4],但是简单地混合等摩尔的反应物水溶液就可以得到浓度约48 %的过氧甲酸溶液。可以通过蒸馏将过氧甲酸的浓度提高至约90 %[4]。
使用催化剂可以大规模地进行工业生产,但反应温度需控制在80 - 85 °C以下以防爆炸[11]。催化剂可使用硝酸、氢氟酸、磷酸、硫酸或其盐[4][12];或是含有酯基的有机物,如羧酸酯[13]、过氧乙酸[8]。
安全性
[编辑]过氧甲酸无毒,但对皮肤有刺激性(弱于过氧乙酸)。浓品(50 %以上)有强反应性,受热易分解,快速加热时会爆炸。室温下与甲醛、苯甲醛、苯胺等易燃物混合时可能会燃烧或爆炸,遇金属粉末会剧烈反应,乃至爆炸[4]。
因此,处置泄漏的过氧甲酸需及时用冷水稀释,并用中性、不可燃的无机吸附剂(如蛭石)吸收[5]。
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014: 749. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001.
- ^ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Elvers, B. et al. (ed.) (1991) Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 5th ed. Vol. A19, Wiley, p. 206
- ^ F. A. Carroll Perspectives on Structure and Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Wiley-Interscience, 2010, ISBN 0-470-27610-X p. 416
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Swern, Daniel. Organic Peracids.. Chemical Reviews. 1949, 45: 1. doi:10.1021/cr60140a001.
In the absence of catalysts, performic acid explodes when heated rapidly to 80–85°C.
- ^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Pradyot Patnaik A comprehensive guide to the hazardous properties of chemical substances (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆), Wiley-Interscience, 2007, ISBN 0-471-71458-5, p. 128
- ^ Simpson, R. J. Performic Acid Oxidation of Proteins. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2007, 2007: pdb.prot4698. doi:10.1101/pdb.prot4698.
- ^ Gehr, R; Chen, D; Moreau, M. Performic acid (PFA): tests on an advanced primary effluent show promising disinfection performance (PDF). Water Science and Technology. 2009, 59 (1): 89–96. PMID 19151490. doi:10.2166/wst.2009.761. (原始内容 (PDF)存档于2010-11-16).
- ^ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Preuss, A., Fuchs, R., Huss, M. & Schneider, R. 2001 Aqueous Disinfecting Agent Containing Performic Acid and Peracetic Acid Process for Production and Process for Use Thereof 美国专利第6,211,237号, Issue date: April 3, 2001
- ^ Bydzovska, O. & Merka, V. Disinfecting Properties of Performic Acid Against Bacteriophage (X 174 as a Model of Small Envelope-free Viruses. J. Hygiene, Epidemiology Microbiology and Immunology. 1981, 25 (4): 414–423. PMID 6459365.
- ^ Ripin, D.H.B.; et al. Execution of a Performic Acid Oxidation on Multikilogram Scale. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2007, 11: 762. doi:10.1021/op700039r.
- ^ Elvers, B. et al. (ed.) (1991) Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 5th ed. Vol. A12, Wiley, p. 16
- ^ English, James; Gregory, J. Delafield. Performic Acid Hydroxylation of a,p-Unsaturated Acids and Esters. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1947, 69: 2120. doi:10.1021/ja01201a016.
- ^ Matilla, T. and Aksela, R. 2000 Method for the Preparation of Aqueous Solutions Containing Performic Acid as Well as Their Use. 美国专利第6,049,002号, Issue date: April 11, 2000


