File:Heavy Rains in Southern Japan.gif
外观
Heavy_Rains_in_Southern_Japan.gif (320 × 240像素,文件大小:8.35 MB,MIME类型:image/gif、循环、268帧、8.0秒)
文件历史
点击某个日期/时间查看对应时刻的文件。
| 日期/时间 | 缩略图 | 大小 | 用户 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
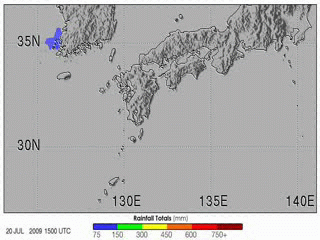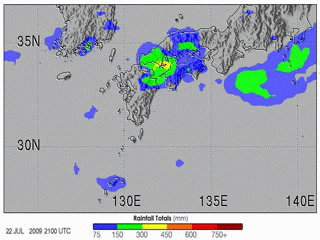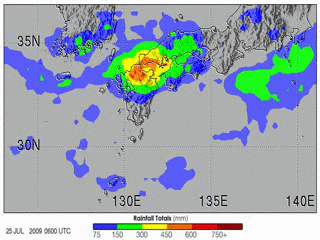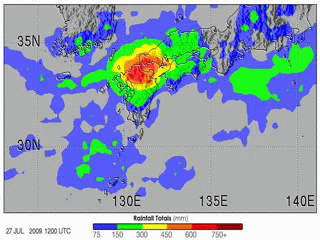
| 当前 | 2009年7月31日 (五) 21:56 |  | 320 × 240(8.35 MB) | Originalwana | {{Information |Description={{en|1=The 2009 summer monsoon brought torrential rains to south western Japan in July. This animatin shows rainfall estimates for southern Japan and the surrounding region from July 20–27. The most prominent feature is a larg |
文件用途
以下2个页面使用本文件:
全域文件用途
以下其他wiki使用此文件:
- cs.wikipedia.org上的用途
- en.wikipedia.org上的用途
- fi.wikipedia.org上的用途
- id.wikipedia.org上的用途
- ja.wikipedia.org上的用途
- ms.wikipedia.org上的用途
- si.wikipedia.org上的用途
- te.wikipedia.org上的用途
- uk.wikipedia.org上的用途
- vi.wikipedia.org上的用途
- www.wikidata.org上的用途